# Wireless capturing
Goal
- Capture, analyze and decrypt wireless traffic.
Used hardware
- Alfa AWUS036NHA (Long-range USB Adapter)
- 1 laptop with Kali Linux
Used software
- Kali Linux (2020.1)
Setup
Getting started
- Display the list of available adapters. (Kali Linux)
kali@kali:~# sudo airmon-ng PHY Interface Driver Chipset phy0 wlan0 iwlwifi Intel Corporation Centrino Advanced-N 6205 [Taylor Peak] (rev 34) phy1 wlan1 ath9k_htc Qualcomm Atheros Communications AR9271 802.11n kali@kali:~#1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8Monitor mode allows a wireless network interface controller to monitor all traffic received on a wireless channel.
- Kill the network managers. (To Avoid interference with other tools)
kali@kali:~# sudo airmon-ng check kill Killing these processes: PID Name 643 wpa_supplicant kali@kali:~#1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8- Put the adapter in monitor mode.
kali@kali:~# sudo airmon-ng start wlan1 PHY Interface Driver Chipset phy0 wlan0 iwlwifi Intel Corporation Centrino Advanced-N 6205 [Taylor Peak] (rev 34) phy1 wlan1 ath9k_htc Qualcomm Atheros Communications AR9271 802.11n (mac80211 monitor mode vif enabled for [phy1]wlan1 on [phy1]wlan1mon) (mac80211 station mode vif disabled for [phy1]wlan1) kali@kali:~#1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12Start Wireshark and select the wlan1mon interface.
kali@kali:~# sudo wireshark1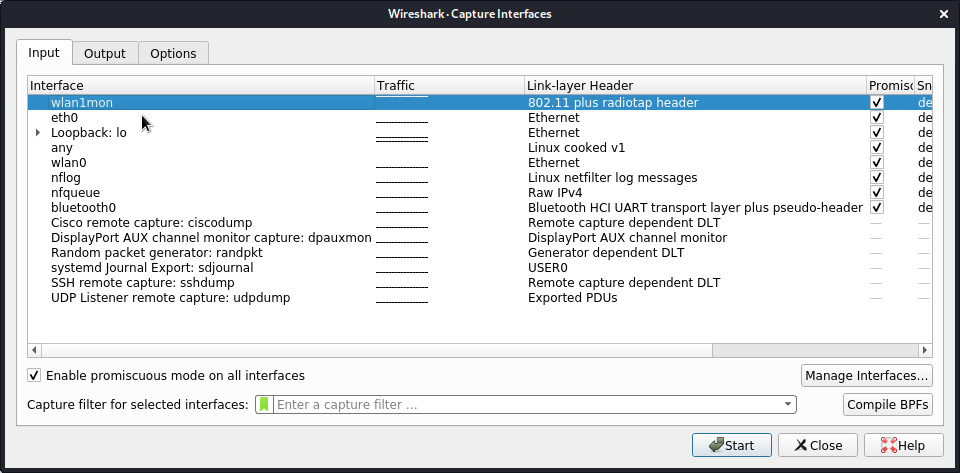
- Check the result.
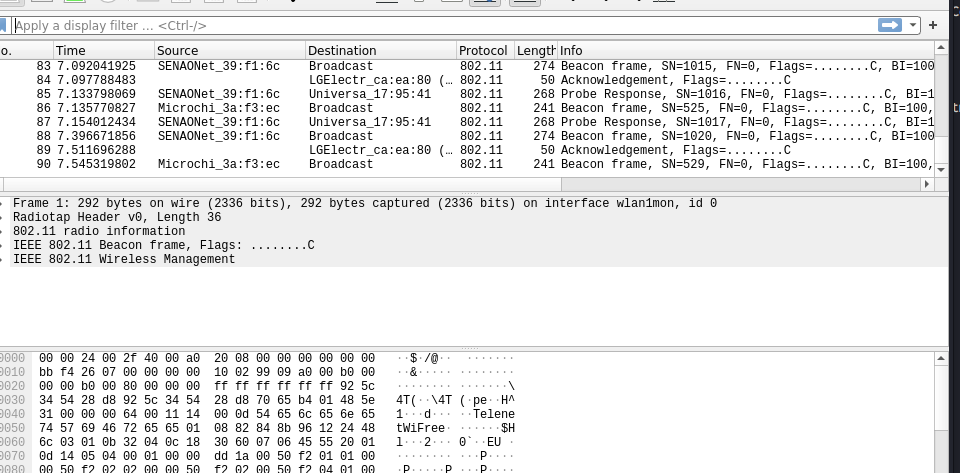
Decrypt wireless traffic in Wireshark.
Go to Edit -> Preferences -> Protocols -> IEEE 802.11.
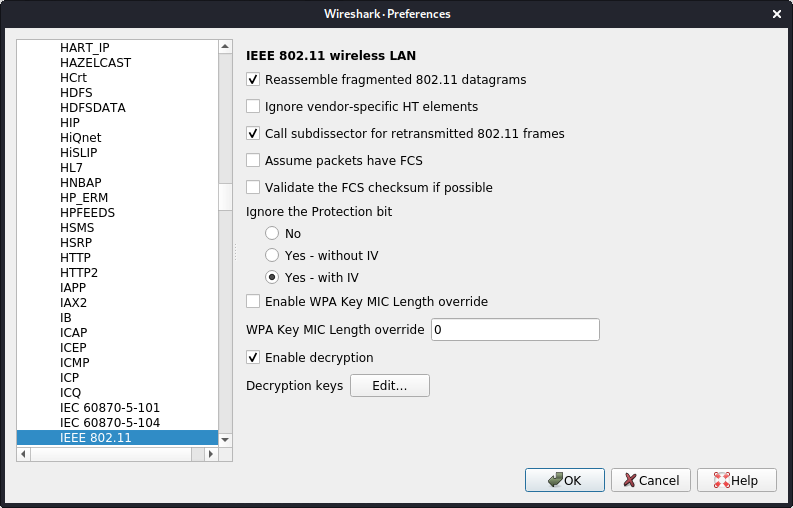
Click on the "Edit..." button next to "Decryption Keys" to add keys.
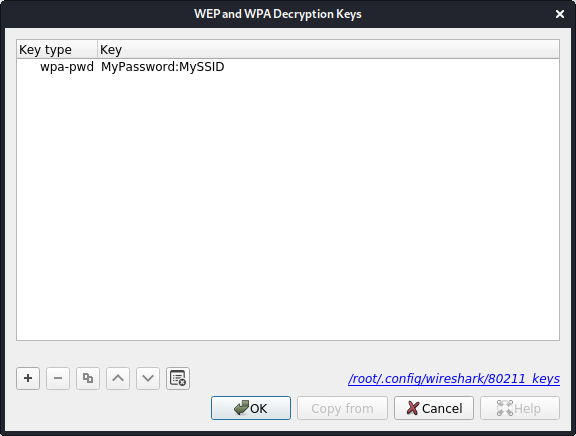
Check the decrypted wireless traffic
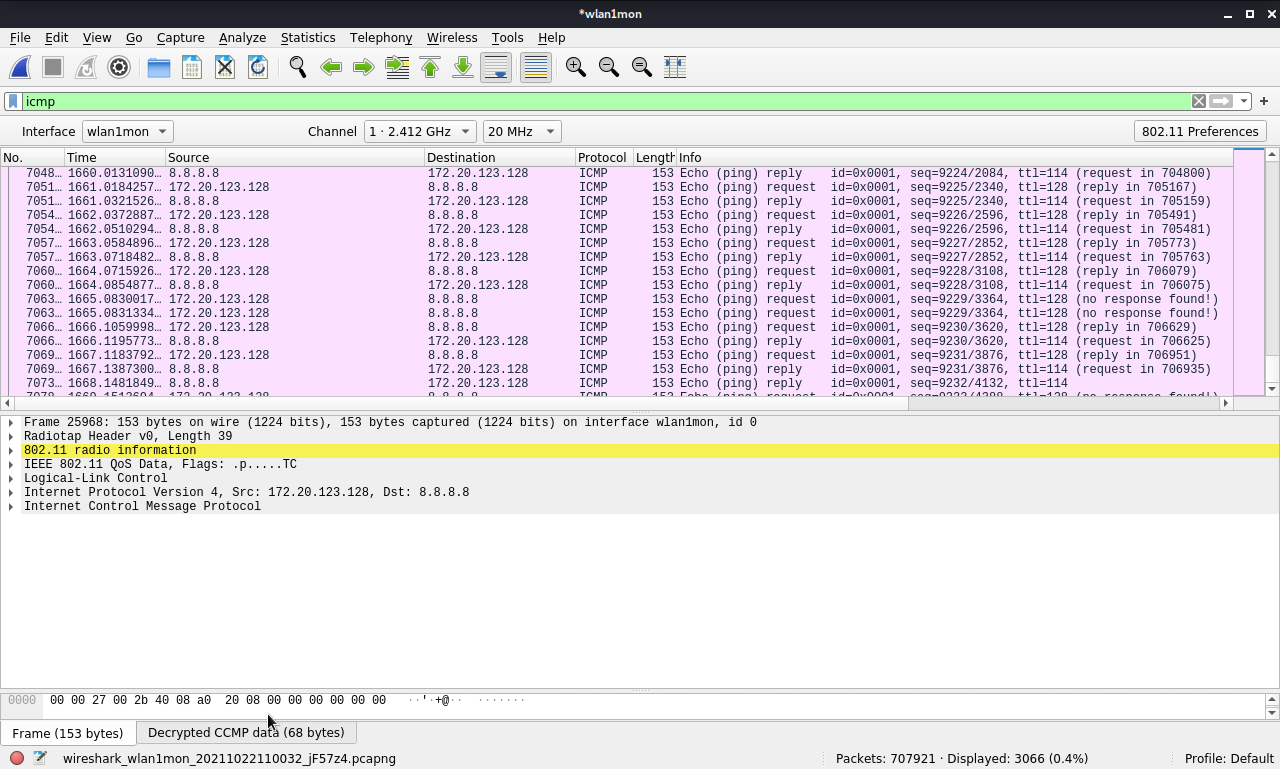 More information about decrypting IEEE 802.11 (opens new window)
More information about decrypting IEEE 802.11 (opens new window)
Conclusion
- It is perfectly possible to capture wireless networks cheaply.